What are the 4 stages of COPD?
What is Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)?
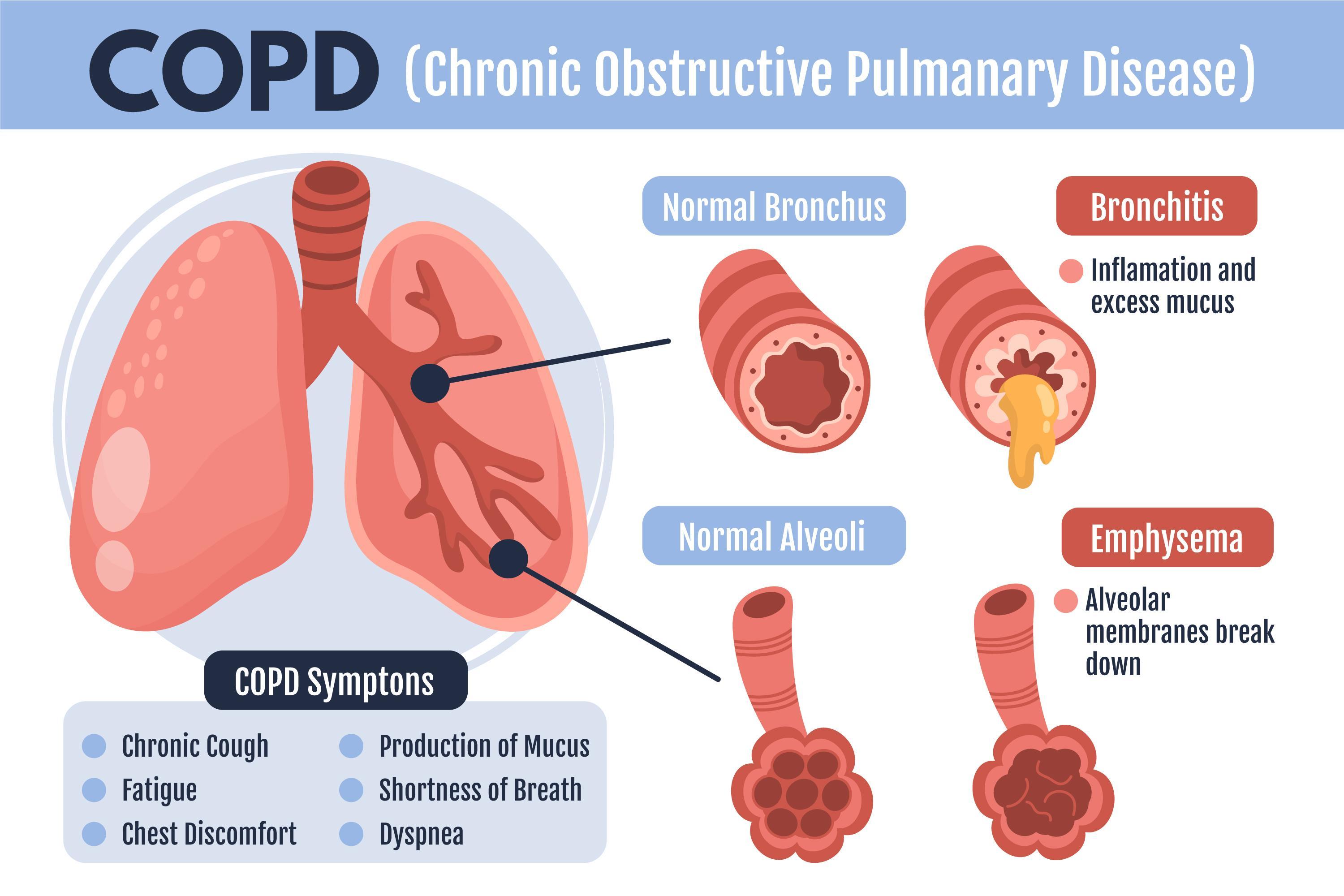
"Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease" (COPD) is a term used to describe certain types of irreversible damage to the lungs and airways that block (obstruct) the airways and make breathing difficult. If you are diagnosed with emphysema or chronic bronchitis, you have COPD.
Changes in the lungs and airways that occur in COPD include:
- Loss of elasticity of the airways and lung alveoli.
- Inflammation, scarring (fibrosis), and narrowing of the airways.
- Thick mucus in the airways.
- Destruction of the walls between the alveoli. This dilates them and traps air.
People with COPD often experience flare-ups or worsening of symptoms, such as severe shortness of breath, thickened mucus, wheezing, and coughing. Hospitalization may be necessary if flare-ups are severe.
COPD progressively worsens over time. Flare-ups become more severe and occur more frequently. This usually occurs over years or decades, although some people experience more rapid progression.
Types of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
COPD includes both emphysema and chronic bronchitis. People with COPD often exhibit characteristics of both.
- Emphysema occurs when the air sacs (alveoli) become damaged and dilated. The most common symptom is shortness of breath (dyspnea).
- Chronic bronchitis is an inflammation of the large airways. This narrows the airways and produces a lot of mucus. Coughing is the most common symptom.
Stages of COPD and their symptoms
Stage 1: Initial
Stage 1 COPD is considered mild. At this stage, you may not be aware that you have lung function problems. Your doctor will classify you as having stage 1 COPD if your FEV1 is between 80% and 100% predicted.
Symptoms
If your spirometry score is stage 1, you may have no obvious symptoms. If symptoms do occur, they may include coughing and increased mucus production. The early stages of COPD can be confused with the flu.
Treatment
In stage 1 COPD, your doctor may recommend a bronchodilator to open your airways. These medications are typically administered via inhaler or nebulizer.
Your doctor may also recommend influenza, COVID-19, and pneumonia vaccines to prevent illnesses that can worsen respiratory symptoms.
Modifying lifestyle habits that led to the development of COPD can help slow its progression.
Stage 2: Mild
COPD is considered stage 2 when the FEV1 drops from 50% to 79% of the predicted value.
Symptoms
During stage 2, symptoms worsen compared to stage 1. Cough and mucus production may worsen, and you may experience shortness of breath when walking or exercising. It's typically at this stage that people realize something is wrong and seek medical attention.
Treatment
You may be given bronchodilators to increase airflow to your lungs.
Your doctor may recommend pulmonary rehabilitation, a program designed to increase your awareness of your condition. It usually takes the form of a group class where you learn how to better manage your condition.
If you experience a flare-up of symptoms, you may need steroids or oxygen.
Stage 3: Severe
At stage 3, COPD is considered severe, and your forced expiratory volume is between 30 and 50% of the expected value. You may have difficulty catching your breath during household chores and may be unable to leave the house.
Symptoms
As you reach stage 3, you may have more frequent flare-ups, and your shortness of breath and cough often worsen. You'll likely notice that you tire more easily than before.
Other potential symptoms may include:
- Frequent colds or nausea
- Ankle swelling
- Chest tightness
- Difficulty breathing deeply
- Wheezing
Treatment
Treatment options for stage 3 COPD are similar to those for stage 2. Oxygen therapy is more likely to be needed at this stage.
Stage 4: Very Severe
Stage 4 is considered very severe. Forced expiratory volume is less than 30% of its normal value, and blood oxygen levels are also low. You are at risk of developing COPD complications, such as heart or lung failure.
Symptoms
In stage 4, you are likely to experience frequent exacerbations that can be life-threatening. You may experience shortness of breath even at rest.
Treatment
Treatment options during stage 4 are similar to those for previous stages. Your doctor may also recommend lung surgery to improve breathing. Surgical options include:
- Lung transplant
- Lung volume reduction surgery
- Bullectomy
For more information visit our site: Genericpharmamall
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Games
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness



