ntroduction:
In the realm of foam plastics, two contenders stand out with distinct compositions, uses, and environmental impacts. Expanded Polypropylene (EPP) foam and ordinary Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) foam cater to diverse applications, each boasting unique characteristics. In this blog post, we delve into the dissimilarities between these foam materials, shedding light on their properties, applications, and environmental implications.
EPP Foam: A Closer Look
Expanded Polypropylene, abbreviated as EPP, represents a new wave of foam plastics with notable eco-friendly attributes. The closed-cell structure of EPP particles, comprising 2% to 10% solid phase components and the rest gas, sets it apart. Key characteristics of EPP foam include:
Lightweight and Elasticity:
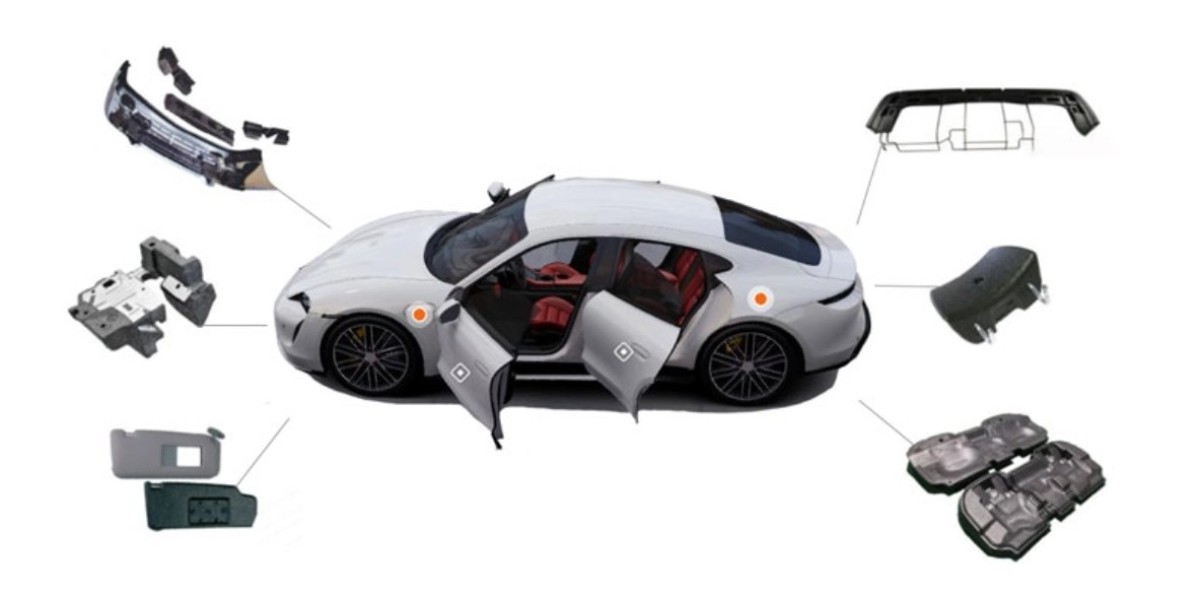
Low specific gravity, excellent elasticity, seismic resistance, and high deformation recovery rate.Widely utilized in critical components of aircraft and automobiles, contributing to fuel efficiency and passenger safety.
Heat Resistance and Insulation:
Heat resistance ranging from -40 to 130℃ with a significant insulation effect.Closed-cell structure provides effective insulation (thermal conductivity coefficient of only 0.038), making it suitable for applications in food packaging and microwave heating.
Recyclability:
100% recyclable due to its pure hydrocarbon composition.Environmentally friendly, as it does not contain harmful additives; digestion leaves only water and carbon dioxide.
Applications:
Used in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and food packaging.EPP pipes employed for transporting warm and cold air due to their food-grade safety and environmental benefits.
Ordinary EPS Foam: The Conventional Choice
Ordinary foam, often referred to as EPS foam or Expanded Polystyrene, serves a more limited range of applications compared to EPP. Key features of EPS foam include:
Application Range:
Primarily used in packaging and construction sectors.Widely employed for wall insulation, flat concrete roof, steel structure roof insulation, and moisture-proof insulation in various fields.
Durability and Cost-Effectiveness:
Known for its durability, making it a preferred choice in construction applications.Recognized as a cost-effective and high-quality thermal insulation and moisture-proof material in the construction industry.
Environmental Considerations:
Not environmentally friendly; challenges with biodegradability.Despite environmental concerns, EPS foam remains widely used in construction due to its durability and cost-effectiveness.

Feininger: Pioneering XPS Technology
Amidst the foam landscape, Feininger emerges as a trailblazer in the field of XPS (Extruded Polystyrene) technology. Established in 2001, Feininger covers an expansive 70-acre area and stands as the first professional manufacturer of XPS Extrusion Line and XPS Foam Board in China.
Conclusion:
In the ongoing debate between EPP and EPS foam, the choice boils down to the specific requirements of the application. EPP foam shines in terms of eco-friendliness, recyclability, and versatility, while EPS foam remains a stalwart in construction applications, balancing durability and cost-effectiveness. As industries evolve, the quest for sustainable and efficient materials persists, with companies like Feininger leading the way in technological innovation and environmental responsibility.










